Setting up a freshwater aquarium brings the fascinating world of aquatic life into your home. While many beginners feel overwhelmed by the technical aspects of aquarium setup, breaking down the process into manageable steps makes it achievable. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything from initial setup to maintaining a thriving ecosystem.
Understanding Your Aquarium System
Before diving into setting up a freshwater aquarium, it’s crucial to understand how an aquatic ecosystem functions. Your aquarium is more than just a container of water; it’s a complex environment where beneficial bacteria, plants, and fish work together to create a balanced habitat.
The Nitrogen Cycle: Foundation of Aquarium Health
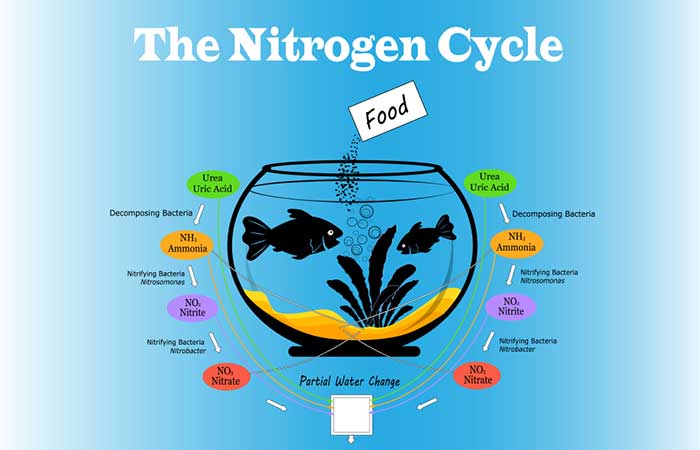
The nitrogen cycle is the cornerstone of a healthy aquarium. Fish produce ammonia through waste and respiration, which is toxic even in small amounts. In a properly cycled tank, beneficial bacteria convert this ammonia into nitrites (also toxic) and then into nitrates (less harmful in moderate levels).
Critical Stages of the Nitrogen Cycle:
- Ammonia Stage (NH3/NH4+): Levels should always read 0 ppm in an established tank
- Toxic above 0.25 ppm
- Can cause gill damage and death
- First to appear in new tanks
- Nitrite Stage (NO2-): Should also read 0 ppm in healthy tanks
- Extremely toxic to fish
- Can cause brown blood disease
- Appears as ammonia converts
- Nitrate Stage (NO3-): Safe below 20 ppm
- Less toxic but still harmful in high concentrations
- Removed through water changes
- Can fuel algae growth if too high
Essential Equipment Selection

Successful aquarium keeping starts with proper equipment selection. Each piece of equipment plays a vital role in maintaining water quality and creating a suitable environment for aquatic life.
Core Equipment Requirements:
Essential Equipment Selection
Setting up a freshwater aquarium requires careful equipment selection. Each component works together to create a healthy environment for your aquatic life. Let’s explore the different filtration options available for your setup.
Understanding Filtration Systems
Every aquarium needs three types of filtration: mechanical, biological, and chemical. Your aquarium filter should cycle your entire tank volume at least four times per hour for optimal results.
Hang on Back (HOB) Filters
Perfect for beginners and tanks under 75 gallons:
- Benefits:
- Easy maintenance and cleaning
- Affordable initial cost
- Creates beneficial surface agitation
- Quick media replacement
- Great for most community tanks
Canister Filters
Ideal for larger tanks and planted aquariums:
- Advantages:
- Multiple media chambers for customization
- Powerful flow rates
- Hidden from view
- Excellent for tanks 40+ gallons
- Superior mechanical filtration
Internal Filters
Best for small tanks and breeding setups:
- Features:
- Space-saving design
- Adjustable flow rates
- Good for tanks under 20 gallons
- Easy installation
Sponge Filters
Perfect for fry and shrimp tanks:
- Unique Benefits:
- Gentle filtration
- Excellent biological filtration
- Safe for small creatures
- Very cost-effective
Choosing the Right Filter
Consider these factors when selecting your filtration system:
- Tank Size and Stock Level
- Calculate total bioload
- Consider future stocking plans
- Factor in plant requirements
- Maintenance Requirements
- Access for regular cleaning
- Media replacement costs
- Time commitment needed
- Noise Considerations
- Location of tank
- Household sensitivity
- Equipment sound levels
Heating Systems

An aquarium heater maintains stable temperatures critical for tropical fish health. Position your heater near water flow for even heat distribution. Essential heating considerations include:
- Calculate 3-5 watts per gallon of water
- Install reliable aquarium thermometers in multiple locations
- Consider a heater guard for fish safety
- Monitor temperature fluctuations regularly
Lighting Systems

Selecting the right aquarium lighting system significantly impacts both plant growth and fish health. While LED aquarium lighting has become the standard for modern setups, understanding all available options helps you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
LED Lighting Systems
LED aquarium lighting leads the market due to its efficiency and versatility. Modern systems provide:
- Customizable spectrum control for optimal plant growth
- Programmable timing with sunrise/sunset effects
- Energy efficiency with minimal heat output
- Longevity of 50,000+ hours of operation
- Lower long-term operating costs
T5 Fluorescent Systems
Still popular among planted tank enthusiasts, T5 lighting offers:
- High light output for demanding plants
- Even light distribution across the tank
- Bulb options for specific plant needs
- Affordable initial setup costs
- Easy bulb replacement every 12-18 months
Metal Halide Systems
Though less common in home aquariums, metal halide lights provide:
- Intense light penetration for deep tanks
- Shimmer effect that mimics natural sunlight
- Excellent growth for light-demanding plants
- Wide area coverage for larger aquariums
Choosing Your Lighting System:
- Consider your tank depth – deeper tanks need stronger lighting
- Factor in plant requirements – low, medium, or high light plants
- Calculate operating costs including bulb replacement
- Plan for heat management, especially with older systems
- Consider adding a timer for consistent light cycles
Essential Maintenance Tips:
- Clean light fixtures monthly to maintain intensity
- Replace bulbs according to manufacturer schedules
- Monitor algae growth and adjust duration if needed
- Start with 6-8 hours of light daily and adjust as needed
- Consider a midday break in lighting to reduce algae
Water Chemistry and Parameters
Setting up a freshwater aquarium requires a thorough understanding of water chemistry. Maintaining proper parameters not only keeps your fish healthy but also supports beneficial bacteria and plant growth. Let’s explore each crucial parameter and how to maintain it.
Essential Water Parameters
pH Levels
pH measures how acidic or alkaline your water is, with 7.0 being neutral. Most freshwater fish thrive in pH ranges between 6.5 and 7.5. However, some considerations include:
- Community tanks generally do best at neutral pH (7.0)
- South American fish often prefer slightly acidic conditions (6.0-6.8)
- African cichlids thrive in alkaline water (7.8-8.4)
- Sudden pH changes are more harmful than slightly suboptimal levels
Water Hardness
Water hardness affects fish health and plant growth. Both GH (General Hardness) and KH (Carbonate Hardness) play crucial roles:
General Hardness (GH)
- Measures dissolved calcium and magnesium
- Ideal range: 4-12 dGH for most community tanks
- Affects fish osmotic regulation
- Essential for invertebrate shell development
Carbonate Hardness (KH)
- Buffers against pH swings
- Recommended range: 4-8 dKH
- Helps stabilize the nitrogen cycle
- Critical for plant growth
Temperature Control
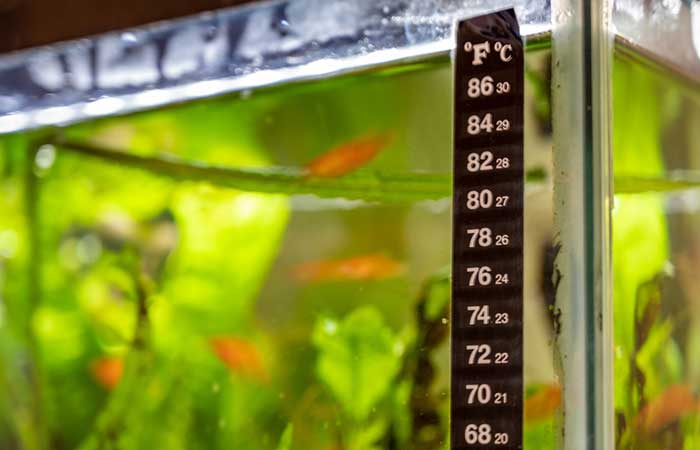

Maintaining stable temperature is crucial for fish health. Your aquarium heater and thermometer work together to ensure consistency:
- Tropical community tanks: 75-80°F (24-27°C)
- Goldfish and cold water species: 65-75°F (18-24°C)
- Plant growth optimum: 75-78°F (24-26°C)
- Avoid temperature fluctuations exceeding 2°F per day
Common Water Issues and Solutions
High Ammonia Levels
Ammonia spikes often occur in new tanks or during cycle crashes. Warning signs and solutions include:
- Fish gasping at the surface
- Red or inflamed gills
- Lethargy and loss of appetite
- Immediate actions:
- Perform 50% water change
- Add ammonia-neutralizing products
- Reduce feeding
- Check filter function
Nitrate Management
High nitrate levels indicate the need for maintenance adjustments:
- Optimal level: Below 20ppm
- Warning signs:
- Rapid algae growth
- Plant leaves turning yellow
- Fish showing stress symptoms
- Solutions:
- Regular water changes
- Add fast-growing plants
- Reduce stocking levels
- Improve filtration maintenance
Substrate Selection and Aquascaping

Setting up a freshwater aquarium’s foundation begins with choosing the right substrate. Your choice affects water chemistry, plant growth, and the overall aesthetic of your aquatic environment.
The Cycling Process: Establishing Your Ecosystem
Setting up a freshwater aquarium requires proper cycling to establish beneficial bacteria. This process typically takes 2-4 weeks and is crucial for long-term success. Understanding each phase helps prevent common mistakes that often lead to fish loss.
Understanding the Cycling Phases
Phase 1: Ammonia Introduction
The first step in cycling requires an ammonia source to feed beneficial bacteria:
- Methods to Start the Cycle:
- Pure ammonia dosing (recommended)
- Add 2-4 ppm ammonia
- Test daily until levels drop
- Maintain consistent temperature
- Fish food method
- Add small amounts daily
- Monitor decomposition
- Less precise but effective
- Pure ammonia dosing (recommended)
Phase 2: Nitrite Spike
As ammonia-converting bacteria establish, you’ll notice:
- Signs of Progress:
- Ammonia levels dropping
- Nitrite readings appearing
- Possible cloudy water (bacterial bloom)
- Monitoring Requirements:
- Test ammonia and nitrites daily
- Maintain water temperature
- Check pH stability
Common Cycling Problems and Solutions
- Stalled Cycle
- Causes:
- pH below 7.0
- Temperature fluctuations
- Insufficient oxygen
- Solutions:
- Adjust pH with aquarium buffer
- Stabilize temperature
- Increase surface agitation
- Causes:
- Crashed Cycle
- Warning Signs:
- Sudden ammonia spike
- Loss of nitrate readings
- pH swings
- Recovery Steps:
- Large water change (50%)
- Add beneficial bacteria supplements
- Check filter media condition
- Reset ammonia levels to 2ppm
- Warning Signs:
Confirming Cycle Completion
Your aquarium is cycled when:
- Test Results Show:
- 0 ppm ammonia
- 0 ppm nitrites
- Detectable nitrates (5-20 ppm)
- Verification Process:
- Add small ammonia dose
- Test after 24 hours
- Should read 0 ammonia and 0 nitrites
Adding Life to Your Aquarium: Fish and Plant Selection
After successfully setting up a freshwater aquarium and completing the cycling process, it’s time to add aquatic life. Starting with plants and following a careful stocking plan ensures the best success rate for your new ecosystem.
Beginning with Live Plants
Adding plants before fish helps stabilize your aquarium and provides natural shelter. Consider these beginner-friendly options:
Easy Starter Plants
- Anubias Species
- Extremely hardy
- Grows in low light
- Attach to driftwood or rocks
- Resistant to algae
- Java Fern Varieties
- Low maintenance
- Propagates easily
- Tolerates various water conditions
- Provides excellent cover for fish
- Amazon Sword
- Fast-growing background plant
- Benefits from root tabs
- Creates natural territories
- Oxygen producer
Fish Selection and Introduction
Hardy Starter Fish
Begin with peaceful, hardy species that can handle varying water conditions:
- Recommended First Fish:
- Zebra Danios
- Active swimmers
- Temperature range: 64-77°F
- School of 6+ recommended
- Platies
- Colorful varieties available
- Peaceful community fish
- Good for water quality monitoring
- Corydoras Catfish
- Bottom cleaners
- Social groups of 4+
- Help maintain substrate
- Zebra Danios
Proper Acclimation Process
Careful acclimation reduces stress and improves survival rates:
- Temperature Acclimation
- Float bag for 15-20 minutes
- Match temperature gradually
- Avoid sudden changes
- Water Chemistry Adjustment
- Add small amounts of tank water to bag
- Every 5 minutes for 30 minutes
- Never add store water to tank
- Use net to transfer fish
Stocking Guidelines
- Follow the One-Inch Rule
- One inch of fish per gallon
- Account for adult fish size
- Consider fish activity levels
- Introduce Fish Gradually
- Wait 1-2 weeks between additions
- Monitor water parameters closely
- Observe existing fish behavior
- Add more active fish first
Ensuring Long-Term Success: Final Guidelines
Setting up a freshwater aquarium is just the beginning of your aquatic journey. Success comes from consistency and attention to detail. Let’s review key practices that will help your aquarium thrive for years to come.
Essential Habits for Thriving Aquariums
Record Keeping
- Maintenance Log
- Track water change dates
- Document parameter readings
- Note equipment maintenance
- Monitor fish behavior changes
- Testing Schedule
- Regular parameter testing
- Track trends over time
- Anticipate potential issues
Equipment Management
- Backup Equipment
- Spare heater
- Extra filter media
- Emergency air pump
- Basic test kits
Continuing Your Aquarium Journey
- Stay Informed
- Join aquarium communities
- Read trusted resources
- Connect with local fish stores
- Share experiences with others
- Future Considerations
- Planning for tank upgrades
- Exploring new species
- Advanced plant keeping
- Aquascaping techniques
Final Thoughts
Setting up a freshwater aquarium creates a living ecosystem that brings beauty and tranquility to any space. Remember that patience and consistency are your greatest allies in this hobby. Start small, learn from each experience, and enjoy watching your underwater world develop and thrive.
Whether you’re creating a peaceful community tank or planning an elaborate planted aquascape, the fundamentals covered in this guide will help ensure your success. Keep learning, stay curious, and most importantly, enjoy the journey of aquarium keeping.






